Male reproductive organ designed to be able to generate, transmit and store sperm. Sperm stored in liquid that protected and nutritious, the semen.
Sperm Production
 Determine the most important part of producing sperm is testis. Head of mature sperm has a oval shape and flat, and has a curls tail that useful to encourage sperm to enter the semen. Head of the sperm has a nucleus with a chromosome and also has a structure called the acrosome that is able to penetrate the layer of jelly that encircle ovum and that fertilize it if necessary. Sperm produced by the organ called testis safely stored in the scrotum. This position keep the testis keep cooler than other part of the body. The establishment of sperm is running low on the normal temperature, but continue to occur at a lower temperature in the scrotum. So, avoid things that cause the temperature around the scrotum to be high because it will affect the quality and quantity of sperm production.
Determine the most important part of producing sperm is testis. Head of mature sperm has a oval shape and flat, and has a curls tail that useful to encourage sperm to enter the semen. Head of the sperm has a nucleus with a chromosome and also has a structure called the acrosome that is able to penetrate the layer of jelly that encircle ovum and that fertilize it if necessary. Sperm produced by the organ called testis safely stored in the scrotum. This position keep the testis keep cooler than other part of the body. The establishment of sperm is running low on the normal temperature, but continue to occur at a lower temperature in the scrotum. So, avoid things that cause the temperature around the scrotum to be high because it will affect the quality and quantity of sperm production.Women's Reproductive System
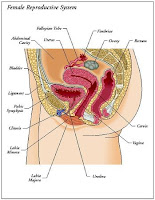 Basically, female reproductive organs consist of ovary (ovarium) and the uterus and the channels associated with both. Uterus is located in the center of the system, uterus has a bag shaped where babies grow. Without the baby inside it, uterus is very small only 7 to 9 cm. On the part of the outside, uterus through the cervix related to the vagina is the entrance of the penis and sperm.
Basically, female reproductive organs consist of ovary (ovarium) and the uterus and the channels associated with both. Uterus is located in the center of the system, uterus has a bag shaped where babies grow. Without the baby inside it, uterus is very small only 7 to 9 cm. On the part of the outside, uterus through the cervix related to the vagina is the entrance of the penis and sperm.Cervix is the lower part of the uterus from the vagina to have the channel. The top of the uterus is fallopian channel. Close to the bottom line is this ovary. Ovary produce about 200 thousand to 400 thousand follicles.
In the uterus called the endometrium, which will be thick during pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur then the layer of endometrium is shed and next period menstruation happened.

Illustration. In the structure of the Uterus
Reproductive Hormones
Hypothalamus and the pituitary gland set reproduction hormones. Hormones consist of:
Hypothalamus produce gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
GnRH stimulates pituitary gland to produce FSH and LH
Estrogen, progesterone and testosterone secreted by ovary.

Illustration. LH and FSH rising during menstrual cycle
Ovulation
A woman will have the ability to reproduce/pregnant after she enters puberty and start experiencing menstruation. The process of fertilization is very complex:
First to known, ovulation only happens one day just in one cycle and when the pregnancy does not occur, two weeks latter followed by a menstrual cycle. Usually, the period between ovulation and next menstruation is not much different. The duration of menstrual cycle is having variation depending on the time since the beginning of the cycle until ovulation.
The length of time since the beginning of menstruation until ovulation can be manifold. Ovulation often delayed at the time someone experiencing stress, during breastfeeding period and pre-menopause.
On a day ovulation in a cycle, one or two ovum cells are ready to be fertilized. Ovum cells do not live more than 24 hours, while the live sperm cells different. If there is no mucus that supports the continuance of his life, sperm cells cannot survive more than one hour or thereabouts. However, with the good cervix mucus, sperm cells can survive up to 2 or 3 days, sometimes even be able to 4 or 5 days.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, FSH stimulates several follicles being mature around 2 weeks until ovum cells approaching the size of three times. Only one follicle that will be the dominant for once cycle.
FSH provides signal to dominant follicle to produce estrogen that would reach the uterus. In the uterus, estrogen stimulates layer of uterus (endometrium) being thicken.
Estrogen reaches to peak around the day-to-14. At that time, estrogen trigger increased LH.
LH has two important roles, that are:
The increase in LH will stimulate the occurrence of ovulation. Ovulation occurs due dominant follicle pushed and release its ovum cell to one of the fallopian channel. In this channel, sperm fertilizes ovum cell.
Broken follicle will close and re-establish the korpus luteum that produces large amounts of progesterone. After 14 days korpus luteum will be destroyed immediately and the next cycle begins, unless if fertilization occurs.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH) produced by pituitary gland. Together with the hormones in the body of the other follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and estrogen, LH menstruasi help set the cycle in women and the occurrence of ovulasi. LH and FSH increased and decreased together menstruasi round of a cycle.
LH increased significantly shortly before the occurrence of ovulasi, normal menstrual cycle for 28 days this will happen in mid-cycle (day-to-14). This event is called the LH surge (increase of LH right)
Illustration. Increased LH and FSH during the cycle menstruasi
Travel fertilized eggs that have been
Immediately after the meeting with egg cells or sperm is called fertilization, the egg cell split itself into two cells. The average time needed about 30 hours after the second ovulasi cells to grow into embryo cells, and is moving down the fallopian channel cavity in the center of the uterus.
Both continue to split the cells themselves produce more cells, called blastomere. Approximately 60 hours after ovulasi, a group of cells (a group of blastomere) or the morula containing about 12 to 16 blastomere from moving toward falopian uterus. Once entering the uterus, the growth of the baby immediately. Furthermore, the fetus naturally stick to the womb.
No comments:
Post a Comment